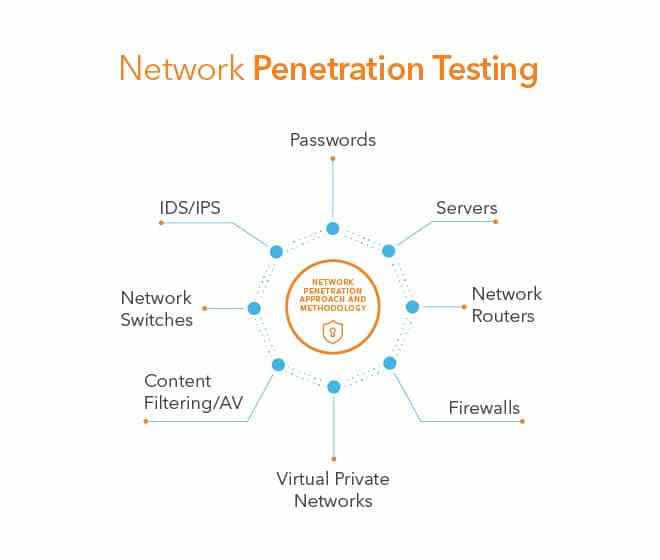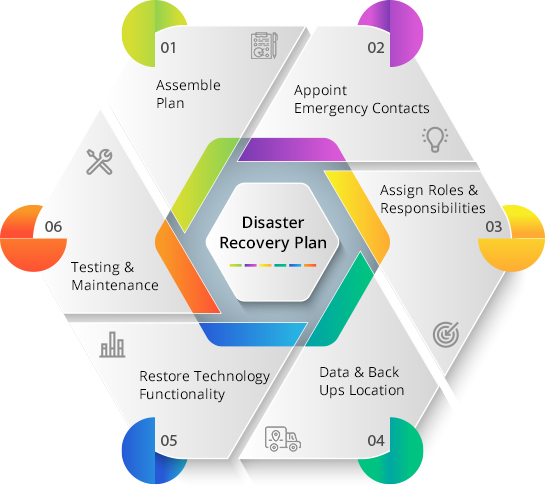
Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery is an organization’s method of regaining access and functionality to its IT infrastructure after events like a natural disaster or cyber attack. A variety of disaster recovery (DR) methods can be part of a disaster recovery plan. DR is one aspect of business continuity.
An Effective Disaster Recovery Plan
Disaster recovery team: This assigned group of specialists will be responsible for creating, implementing and managing the disaster recovery plan.
Risk evaluation: Assess potential hazards: For example, a cyber attack, can you get your data back?
Business-critical asset identification: A good disaster recovery plan includes documentation of which systems, applications, data, and other resources are most critical for business continuity, as well as the necessary steps to recover data.
Back-up: This is the simplest type of disaster recovery and entails storing data off site or on a removable drive. However, just backing up data provides only minimal business continuity help, as the IT infrastructure itself is not backed up.